United States Vibro Hammer Specification Guide – Sheet, Casing, H-Pile
JH KIM
view : 41
U.S. marine, bridge, and metro projects demand a spec-first approach to vibro hammer selection. This guide maps EM (eccentric moment), CF (centrifugal force), VPM (frequency), amplitude, and line-pull to typical American job scenarios (sheet/casing/H-pile), then matches the choice to power packs and clamps so you can move from submittal to RFQ without re-work.
• Vibro Hammer Specification (model tables) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/specification/
• Vibro Hammer Features (suppressor, elastomers, remote pendant) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/features-2/
• Vibratory Hammer Guide (principles & terms) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/blog/vibratory-hammer-guide/
• Vibratory Hammer in Pile Driving (applications) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/blog/vibratory-hammer-pile-driving/
• Contact Us (RFQ) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/contact-us/
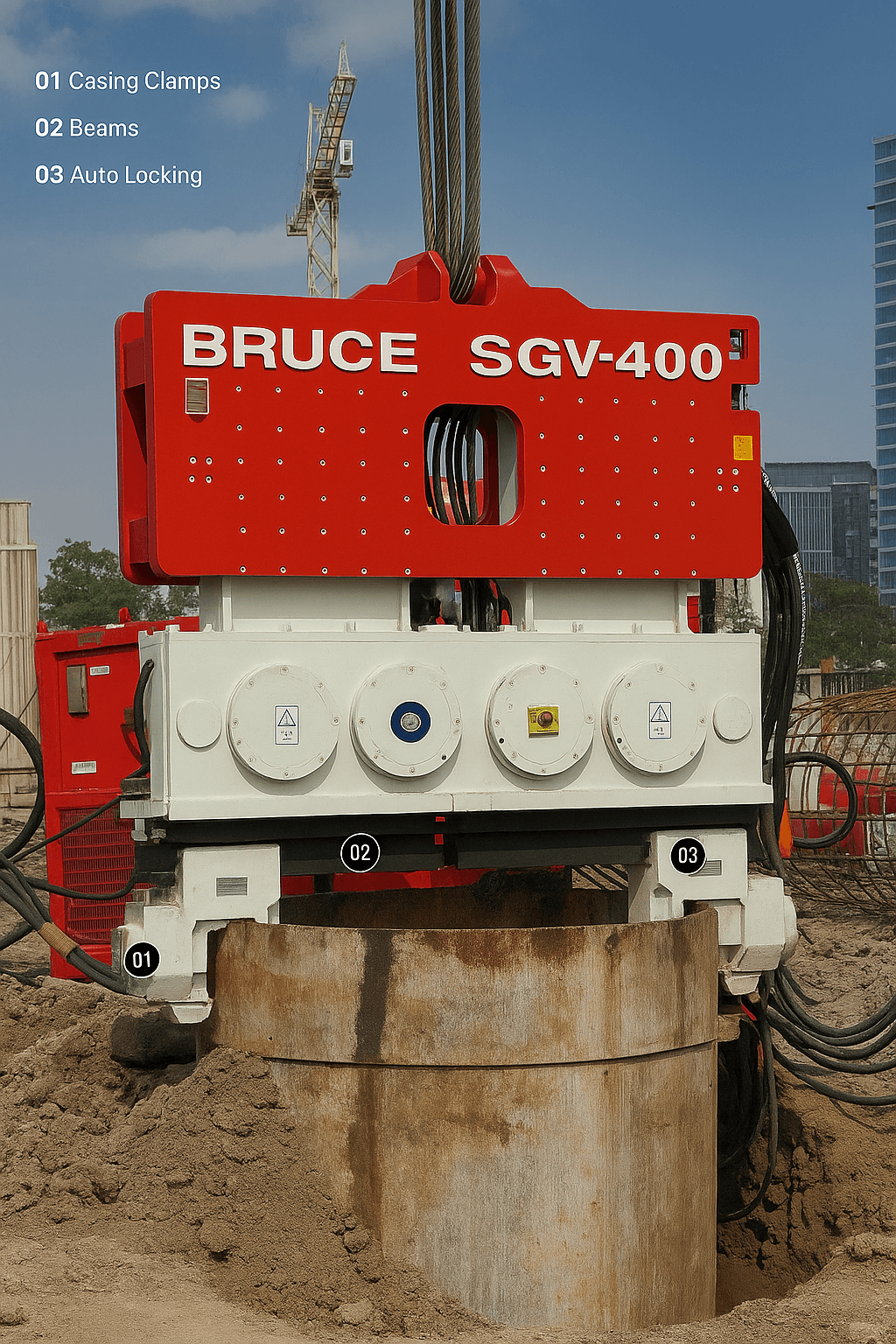
1) Spec baselines by pile type (U.S. jobs)
Sheet piles (urban/bridge cofferdams):
-
· Target: mid–high VPM (≈1,700–2,000) for loose to medium sands; suppressor housing where city noise constraints apply.
· EM/CF: SGV 200–600 class typically covers most SP-III to SP-VI walls; check line-pull for extraction.
· Clamp: Universal sheet clamp sized for section depth; verify check valve + LED clamp-engage.
H-piles (deep foundations, limited headroom):
· Target: mid VPM with higher amplitude retention; ensure jaw profile suits flange thickness.
· EM/CF: step into SGV 400–600 for denser soils; consider power pack flow ceilings.
Casing/pipe piles (marine/offshore, drilled shafts):
· Target: frequency that avoids resonance with casing; double/quad clamps for large diameters, auto-locking beams for quick spans.
· EM/CF: SGV 600–1000–2000 range for heavy steel casings or long pipe piles; confirm max line-pull.
See full EM/CF/VPM tables and clamp ranges → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/specification/
2) U.S. soil response & tuning (VPM / amplitude)
· Loose sands & fills: higher VPM (≈1,900–2,000); keep amplitude moderate to prevent over-liquefaction around the wall toe.
· Dense sands/gravel: reduce to ≈1,600–1,730 VPM, increase amplitude via model step-up (EM/CF) to maintain penetration.
· Mixed/overburden near structures: prioritize suppressor + elastomer stack to limit transmitted vibration; verify monitoring plan.
Reference operating features and tuning controls → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/features-2/
3) Model selector (practical cut-offs)
Start here if you know three inputs: pile type, max section/Ø, target embedment.
· SGV 200–300: urban sheet walls, moderate embedment; short-span river works; tight access.
· SGV 400–600: heavier sheets / H-piles; mixed sands; general bridge foundations.
· SGV 1000: deep marine pipe/casing; higher amplitude demand; tidal windows.
· SGV 2000: very large casings/pipe piles, offshore staging; high CF with robust cooling & power delivery.
Download or view model tables → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/specification/
Brochure visuals & component overview → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/brochure/
4) Clamp & jaw selection (safety + productivity)
· Universal/Sheet Clamp (60U–320U): match clamping force to section and wall friction; check working pressure 300–320 bar.
· Double/Quad Casing Clamp (2×80D…4×160D): use auto-locking beam for diameter swaps; aim for <1 min changeover to save hours/week on large runs.
· Jaw profiles: keep hardened jaw fit to prevent flange crushing; use guide cheeks for precise alignment.
Clamp families and dimensions → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/specification/
5) Power pack matching (flow/pressure/cooling)
· Correct flow (LPM/GPM) and pressure (bar/psi) keep your hammer in its performance band. Pick from PQ-200V to PQ-1600V based on the SGV model and anticipated duty cycle (summer river temperatures, offshore spray, long extraction pulls).
· Rule-of-thumb: never cap the pump flow below the hammer’s max oil flow; sustained under-supply reduces amplitude and increases heat.
· Cooling: larger radiators and oil coolers stabilize high VPM urban runs and offshore shifts.
(See brochure power pack tables) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/brochure/
6) Urban noise & compliance (submittal-ready)
For city centers and rail corridors, plan the package as follows:
· Suppressor/silence housing with elastomer isolation to reduce frame-borne noise.
· IEA/operation logs to document frequency, runtime, clamp-engage events for the owner’s QA.
· Remote pendant emergency stop + clamp status LEDs in operator line-of-sight.
Operating features for submittals → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/features-2/
Principles & terminology refresher → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/blog/vibratory-hammer-guide/
7) Extraction planning (line-pull reserves)
· Temporary works and contaminated soils require conservative extraction planning:
· Check the max line-pull (kN/ton) for your SGV model; size the lifting gear accordingly.
· Plan for reverse-vibration sequences on locked sheets; keep hose routing protected during high-angle pulls.
Spec tables with line-pull → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/specification/
8) Lead time, spares, commissioning (U.S. delivery)
· Typical lead time: project/region dependent; align model and clamp kit early with submittal approvals.
· Spares: jaws, elastomers, hose sets, filters; keep a first-month kit on site.
· Commissioning & training: verify frequency adjust, clamp pressure checks (300–320 bar), and daily inspection routines.
Start your RFQ → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/contact-us/
9) U.S. use-case snapshots (spec-driven picks)
· DOT river bridge cofferdam (sheet piles, medium sands): SGV 400–600 + suppressor; PQ-600V class; universal clamp 130U–160U.
· Harbor pipe piles (Ø large, tidal): SGV 1000; double/quad casing clamp; high-capacity cooling; pendant-based frequency ramp-up.
· Urban H-pile foundations (noise envelope): SGV 300–400 with silence housing; VPM ≈ 1,730–1,900 tuned during monitoring.
10) Technical FAQs (spec & RFQ)
Q1. How do I choose EM/CF?
Start from pile type + embedment; check soils and required amplitude. If penetration stalls at compliant VPM, step up EM/CF before overspeeding.
Q2. Which clamp for mixed programs?
Urban walls + occasional casing: universal sheet clamp as baseline, plus double casing clamp kit with auto-locking beam for one-minute swaps.
Q3. What’s the fastest way to confirm fit?
Send pile type/size, target depth, soil brief, and site constraints (noise, access). You’ll receive a model + power-pack match.
RFQ → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/contact-us/
Contact Us
-
Explore full Vibro Hammer Specification tables (EM/CF/VPM) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/specification/
-
Review Vibro Hammer Features (suppressor, elastomers, pendant, IEA) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/products/vibro-hammer/features-2/
-
Deep dive: Vibratory Hammer Guide (principles, glossary) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/blog/vibratory-hammer-guide/
-
See Vibratory Hammer in Pile Driving (applications, workflows) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/blog/vibratory-hammer-pile-driving/
-
Request a U.S. project recommendation (24-hour response) → https://www.powerquip.co.kr/contact-us/